PART-1
WHAT IS WATER POLLUTION?
Water pollution occurs when harmful substances - like chemicals, plastics, and toxins - contaminate water sources such as rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater. This contamination makes water toxic for aquatic life, humans, and the entire ecosystem.
Polluted water isn't just an environmental issue; it directly threatens our health, causing diseases and disrupting nature's balance. But where does all this pollution come from? Let's dive into the major sources of water pollution.
MAJOR SOURCES OF WATER POLLUTION:
Today, water pollution is a serious environmental issue in India. It has not only affected surface water like rivers, lakes, oceans, etc. But also, the quality of the groundwater. The common pollutants affecting the water in India are:
1. Industrial waste:
Many major cities in India are built along rivers and lakes. While this may seem ideal, industrial waste from these cities is often dumped directly into these water bodies, making them dangerously toxic.
The industrial waste includes:
• Heavy metals (Lead, mercury, arsenic, cadmium) – Released from mining, tanneries, and battery factories.
• Chemical waste – Toxic chemicals from textile, paper, and pharmaceutical industries.
• Oil & grease – Spills from refineries and factories.
• Hospital waste – Unregulated disposal of medical waste.
These pollutants kill aquatic life and make their way into our food and drinking water!
2. Sewage and Domestic Waste
Millions of people depend on stable and large water resources such as rivers, lakes, etc., for daily life, where there is human and domestic animal inhabitation; sewage and domestic waste is routinely generated. Unfortunately, untreated sewage and household waste commonly end up in these waterbodies (Rivers, lakes, etc.)
The Domestic waste contains:
• Untreated sewage – Human and animal waste, household garbage.
• Pathogens & bacteria – Harmful microorganisms like E. coli and parasites that cause deadly waterborne diseases.
Without proper waste treatment, these large waterbodies become breeding grounds for deadly infections affecting humans and animals.
3. Agricultural waste:
Farming is essential for survival, but excessive use of chemicals in agriculture is a silent contributor to water pollution. Let's see how:
• Fertilizer & pesticide runoff:
Chemicals like nitrogen, phosphorus, etc., present in fertilizers and Pesticides sprayed over crops (e.g. DDT, Organophosphates) enter water bodies, leading to toxic algae growth that suffocates aquatic life. It can also contaminate groundwater as well, resulting in water pollution
• Animal Waste:
Livestock operations during agricultural work can generate excreta, pathogens (Bacteria/viruses) and other livestock-related waste. Due to improper disposal, it flows into the nearby waterbodies and contaminates them.
• Sediment runoff:
Activities like tilling and soil erosion from farms clog water bodies, reducing sunlight penetration and harming aquatic ecosystems.
• Saline Drainage:
Excess salts from irrigation seep into groundwater, making this water unfit for consumption.

4. Plastic Waste (The Slow Poison in Our Oceans and Rivers)
Plastic waste (Packaging, bottles, polythene bags, cups, microplastic, etc.) is one of the biggest threats to water bodies. Have you ever seen a plastic bottle floating in a river? Now imagine billions of them. Now, Let's see where this plastic waste comes from:
• Plastic enters water through drains, landfills, and direct dumping.
• Microplastics from synthetic clothing pollute water bodies.
• Marine life suffers as animals get entangled in plastic or mistake it for food.
• Plastic absorbs toxic chemicals and spreads them through water currents.
• Carcinogens present in plastic products can seep into the water and, once they enter the human body, have the potential to cause developmental, reproductive, neurological, and immune disorders.
Even worse, microplastics enter our food chain through seafood, leading to serious health risks!
5. Cultural Waste
Waste generated during cultural events such as offerings, used flowers, garlands, etc are generally immersed in the water which can contribute to pollution; immersion of this water after proper treatment at a specific designated location can solve this problem.
6. Thermal waste
Power plants and industries release hot water into rivers and lakes. It reduces oxygen levels in the water, making it difficult for aquatic life to survive. Many fish species die due to sudden temperature changes.
7. Pharmaceutical and Medical Waste
Have you ever thrown away expired medicines? Many people do, without realizing that pharmaceutical waste can contaminate water.
• Antibiotics and drugs in water bodies contribute to antibiotic resistance in humans.
• Infectious hospital waste can spread deadly diseases if disposed of improperly.
8. Nuclear waste:
Nuclear plants generate radioactive waste that, if dumped into rivers without proper treatment, can have long-term genetic and health effects on humans and animals. Even a small leak can poison water for centuries. Proper disposal is crucial to prevent irreversible damage!
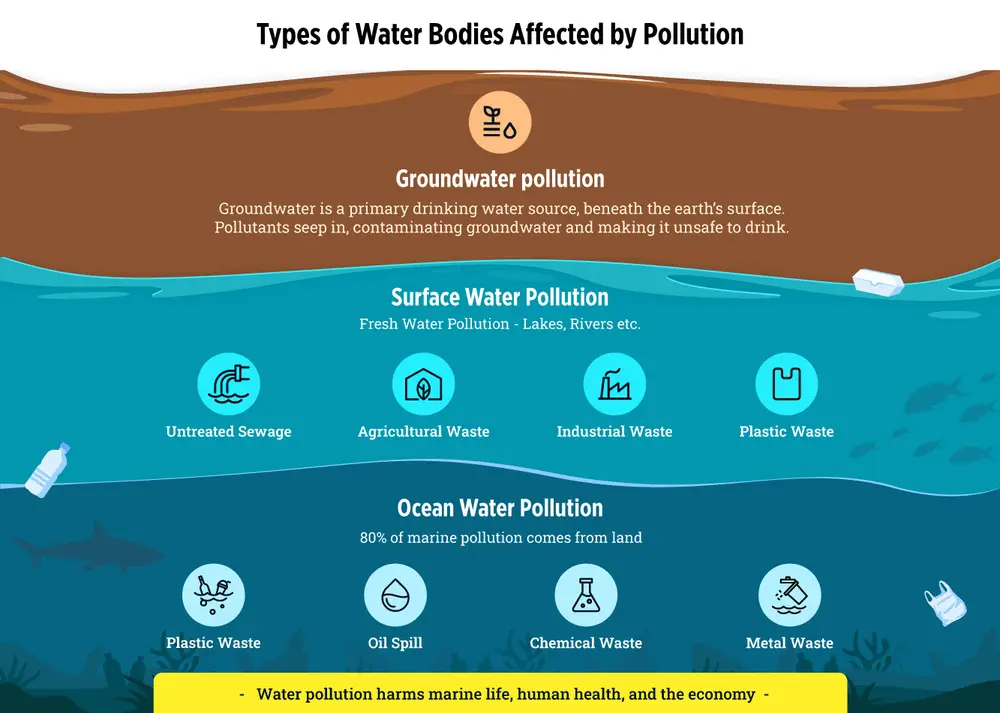
TYPES OF WATER BODIES IMPACTED DUE TO WATER POLLUTION
Groundwater pollution
During the rainy season, rainwater seeps deep into the earth, filling the cracks, crevices, and porous spaces (basically an underground storehouse of water). It is called groundwater, stored beneath the earth's surface and is our main source of drinking water.
Pesticides, chemical fertilizers, and waste from septic systems can seep underground and contaminate this groundwater, making it unsuitable for drinking and human use. Once polluted, groundwater can remain toxic for decades, making it unusable for entire generations.
Surface water pollution
• Freshwater pollution:
Surface water from freshwater resources (sources other than the ocean), such as rivers, lakes, etc., accounts for a significant share of water used for human consumption. Freshwater pollution in India is a major problem. It can get easily contaminated by:
1. Untreated sewage
2. Agricultural waste
3. Industrial waste
4. Plastic and garbage waste, etc.
This contamination of freshwater damages aquatic life affects irrigation, and spreads waterborne diseases among humans.
• Ocean water pollution
Eighty per cent of oceanic water pollution (Marine pollution) originates on land. Industrial waste, chemicals, heavy metals and plastic from cities and farms flow into the ocean through rivers. Oil spills and ship leaks make it worse. Ocean water pollution can harm the marine ecosystem, fisheries, and human health. It can also have a negative impact on the economy.
Water pollution is not just an environmental problem - it's a human crisis. It affects:
• Our health – Contaminated water causes diseases like cholera, dysentery, and cancer.
• Polluted water affects agriculture and marine life, making food unsafe.
• Our future – If we don't act now, clean water may become scarce for future generations.
In the next article, we'll explore the health hazards of water pollution, how to protect ourselves, and ways to prevent this crisis.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.nrdc.org/stories/water-pollution-everything-you-need-know#causes
- https://bbrc.in/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/053-WATER-POLLUTION-IN-INDIA-CAUSES.pdf
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/environmental-science/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2022.880246/full
- https://online.ecok.edu/articles/causes-of-water-pollution/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/water-pollution-and-human-health
- https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/agents/water-poll
- https://www.epa.gov/p2/pollution-prevention-tips-water-conservation
- https://pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=1814499
- https://theiashub.com/upsc/upsc-notes/water-pollution-in-india/

